Medical Marijuana 101
Research is not conclusive on the benefits or risks of medical marijuana use.
Understanding what makes up marijuana and how it may impact our health is an important step in discovering the clinical outcomes of medical marijuana.
The below information is intended to provide a brief overview of medical marijuana in Florida, common medical marijuana terms, ways to consume medical marijuana, and more.
- Medical Marijuana Program in Florida: History and Definitions
- Explanation of Common Terms
- An Introduction to the Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
Medical Marijuana Program in Florida: History and Definitions
In 2016, Florida implemented the Compassionate Medical Use Act, also known as Amendment 2.
This allows patients with a qualifying condition to use medical marijuana after receiving certification from an authorized medical marijuana physician.
OMMU
Established by the Florida Department of Health, the Office for Medical Marijuana Use (OMMU) is charged with writing and implementing the Department of Health’s rules for medical marijuana; overseeing the statewide Medical Marijuana Use Registry; licensing Florida businesses to cultivate, process and dispense medical marijuana; and certifying marijuana testing laboratories.
MMTCs
Often called dispensaries, licensed Medical Marijuana Treatment Centers (MMTCs) are the only businesses in Florida authorized to dispense medical marijuana and low-THC cannabis to qualified patients and caregivers.
Certifying Physician
A physician who is authorized to order low-THC cannabis, medical marijuana or cannabis delivery devices for qualifying patients.
A list of certifying physicians can be located at the OMMU Website.
MMUR
The Medical Marijuana Use Registry (MMUR) is a secure, electronic, online database for the registration of qualified physicians and patients and their orders.
It is accessible by patients, qualified physicians, law enforcement, medical marijuana treatment center staff and Office of Medical Marijuana Use staff.
Conditions
To be eligible for medical marijuana in Florida, you must have one of the following qualifying medical conditions or symptoms:
- Cancer
- Epilepsy
- Glaucoma
- HIV/AIDS
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
- Crohn’s Disease
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Medical condition comparable to those listed
- Terminal condition diagnosed by a physician other than the qualified physician issuing the physician certification
- Chronic nonmalignant pain caused by a qualifying medical condition or that originates from a qualifying medical condition and persists beyond the usual course of that qualifying medical condition
Please note: This page is for informational purposes only, but is not medical or legal advice and should not be used to make healthcare decisions. Please consult your healthcare provider to find out what treatment options are available for you.
Updated May 2021
Explanation of Common Terms
While research is not conclusive about the benefits and risk of medical marijuana, it is helpful to understand what makes up marijuana and what compounds are believed to affect health.
The below information is intended to provide an explanation of common terms that describe marijuana plants and some components of these plants.
Cannabis
Cannabis is the plant used to create hemp and marijuana products.
There are three common cannabis plant species:

Sativa
Tall plant, narrow leaves

Indica
Bushy plant, broad leaves

Ruderalis
Short plant, varied leaves
Hemp
Hemp plants are cannabis species.
Hemp products, however, contain a small amount of the chemical known as “THC” (less than 0.3% THC), which means hemp products are unlikely to have psychoactive effects. Hemp products can be cultivated and sold as of 2018 according to the Federal Agricultural Act.
Marijuana
Marijuana is another word for the cannabis plant.
Marijuana products contain more THC (greater than 0.3% THC) than hemp, and are only legally available through Medical Marijuana Treatment Centers (MMTCs) in Florida.
Cannabinoids
Marijuana contains at least 120 compounds called cannabinoids that cause euphoric feelings or psychoactive effects. The two most common cannabinoids are cannabidiol (CBD) and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
CBD
CBD is a cannabinoid that causes blissful feelings and may reduce certain types of inflammation (swelling).
It is believed to cause a “calm” feeling.
THC
THC is a cannabinoid that causes both blissful feelings and psychoactive effects.
It is believed to cause a “high” feeling.

Terpenes
Marijuana contains compounds called terpenes that produce a distinctive marijuana odor, as well as therapeutic smells like lavender and peppermint.
It is currrently unknown if terpenes play a role in health effects.
Please note: This page is for informational purposes only, but is not medical or legal advice and should not be used to make healthcare decisions. Please consult your healthcare provider to find out what treatment options are available for you.
Updated May 2021
SOURCES:
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine 2017. The Health Effects of Cannabis and Cannabinoids: The Current State of Evidence and Recommendations for Research. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
Medical News Today. 2020. What to know about Terpenes. Accessed from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com
Medical News Today. 2020. What’s the difference between indica and sativa? Accessed from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com
An Introduction to the Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
Your body naturally creates substances called endocannabinoids, and some of these are similar to the cannabinoids found in marijuana.
The body’s ECS sends “signals” (endocannabinoids) to “receivers” (CB1 and CB2 receptors) to help balance your body’s sleep cycle, appetite level, and more.
The cannabinoids in marijuana act in a similar way by connecting to the CB1 and CB2 “receivers” which can lead to different effects (e.g., increased appetite, changes in mood). But cannabinoids in marijuana are not identical to human cannabinoids and they are not the only component of marijuana.
It is not yet completely understood whether and how medical marijuana may help with a number of medical conditions.
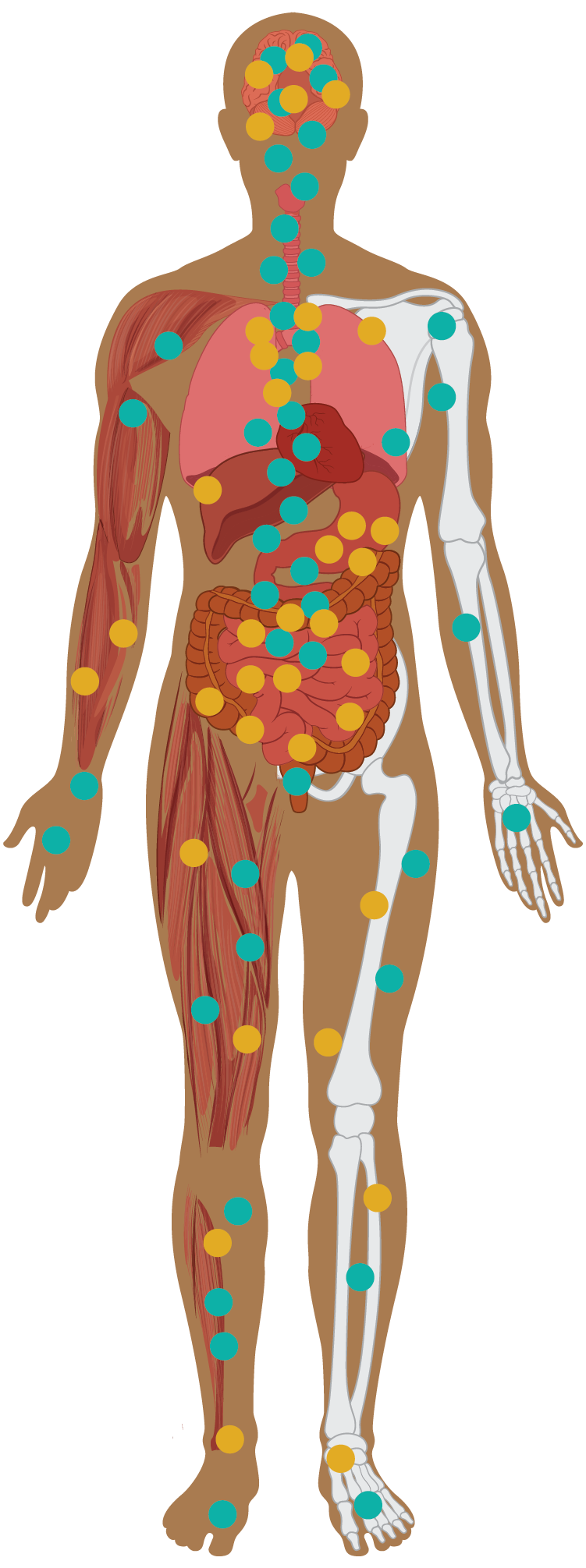
CB1 Receptor
CB2 Receptor
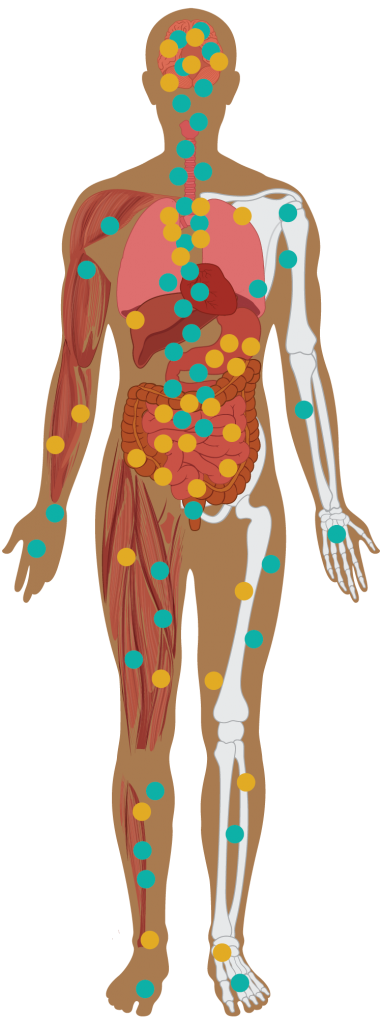
How the Body’s ECS Works
Central Nervous System
Supports the brain and central nervous system including increasing memory

Immune System
Affects the immune system to reduce inflammation.
Hormones
Balances hormones that support metabolism, reproduction, and stress levels.
Digesting Food
Helps control irritation and inflammation in your digestive system.

Muscles
Helps control blood sugar. Creates a feeling similar to a “runner’s high”.

Bones
Supports bone mass and strength.
Please note: This page is for informational purposes only, but is not medical or legal advice and should not be used to make healthcare decisions. Please consult your healthcare provider to find out what treatment options are available for you.
Updated May 2021
SOURCES:
Ligresti A, De Petrocellis L, Di Marzo V. From Phytocannabinoids to Cannabinoid Receptors and Endocannabinoids: Pleiotropic Physiological and Pathological Roles Through Complex Pharmacology. Physiol Rev. 2016;96(4):1593-659.
Wilson RI, Nicoll RA. Endocannabinoid signaling in the brain. Science. 2002;296(5568):678-82.
Zlebnik NE, Cheer JF. Beyond the CB1 Receptor: Is Cannabidiol the Answer for Disorders of Motivation? Annu Rev Neurosci. 2016;39:1-17.
Greenwich Biosciences, Inc. 2019. The Difference Between THC and CBD: Endocannabinoid System. Accessed from www.cannabinoidclinical.com.
- Medical Marijuana Program in Florida: History and Definitions
- Explanation of Common Terms
- An Introduction to the Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
Medical Marijuana Program in Florida: History and Definitions
In 2016, Florida implemented the Compassionate Medical Use Act, also known as Amendment 2.
This allows patients with a qualifying condition to use medical marijuana after receiving certification from an authorized medical marijuana physician.
OMMU
Established by the Florida Department of Health, the Office for Medical Marijuana Use (OMMU) is charged with writing and implementing the Department of Health’s rules for medical marijuana; overseeing the statewide Medical Marijuana Use Registry; licensing Florida businesses to cultivate, process and dispense medical marijuana; and certifying marijuana testing laboratories.
MMTCs
Often called dispensaries, licensed Medical Marijuana Treatment Centers (MMTCs) are the only businesses in Florida authorized to dispense medical marijuana and low-THC cannabis to qualified patients and caregivers.
Certifying Physician
A physician who is authorized to order low-THC cannabis, medical marijuana or cannabis delivery devices for qualifying patients.
A list of certifying physicians can be located at the OMMU Website.
MMUR
The Medical Marijuana Use Registry (MMUR) is a secure, electronic, online database for the registration of qualified physicians and patients and their orders.
It is accessible by patients, qualified physicians, law enforcement, medical marijuana treatment center staff and Office of Medical Marijuana Use staff.
Conditions
To be eligible for medical marijuana in Florida, you must have one of the following qualifying medical conditions or symptoms:
- Cancer
- Epilepsy
- Glaucoma
- HIV/AIDS
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
- Crohn’s Disease
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Medical condition comparable to those listed
- Terminal condition diagnosed by a physician other than the qualified physician issuing the physician certification
- Chronic nonmalignant pain caused by a qualifying medical condition or that originates from a qualifying medical condition and persists beyond the usual course of that qualifying medical condition
Please note: This page is for informational purposes only, but is not medical or legal advice and should not be used to make healthcare decisions. Please consult your healthcare provider to find out what treatment options are available for you.
Updated May 2021
Explanation of Common Terms
While research is not conclusive about the benefits and risk of medical marijuana, it is helpful to understand what makes up marijuana and what compounds are believed to affect health.
The below information is intended to provide an explanation of common terms that describe marijuana plants and some components of these plants.
Cannabis
Cannabis is the plant used to create hemp and marijuana products.
There are three common cannabis plant species:

Sativa
Tall plant, narrow leaves

Indica
Bushy plant, broad leaves

Ruderalis
Short plant, varied leaves
Hemp
Hemp plants are cannabis species.
Hemp products, however, contain a small amount of the chemical known as “THC” (less than 0.3% THC), which means hemp products are unlikely to have psychoactive effects. Hemp products can be cultivated and sold as of 2018 according to the Federal Agricultural Act.
Marijuana
Marijuana is another word for the cannabis plant.
Marijuana products contain more THC (greater than 0.3% THC) than hemp, and are only legally available through Medical Marijuana Treatment Centers (MMTCs) in Florida.
Cannabinoids
Marijuana contains at least 120 compounds called cannabinoids that cause euphoric feelings or psychoactive effects. The two most common cannabinoids are cannabidiol (CBD) and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
CBD
CBD is a cannabinoid that causes blissful feelings and may reduce certain types of inflammation (swelling).
It is believed to cause a “calm” feeling.
THC
THC is a cannabinoid that causes both blissful feelings and psychoactive effects.
It is believed to cause a “high” feeling.

Terpenes
Marijuana contains compounds called terpenes that produce a distinctive marijuana odor, as well as therapeutic smells like lavender and peppermint.
It is currrently unknown if terpenes play a role in health effects.
Please note: This page is for informational purposes only, but is not medical or legal advice and should not be used to make healthcare decisions. Please consult your healthcare provider to find out what treatment options are available for you.
Updated May 2021
SOURCES:
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine 2017. The Health Effects of Cannabis and Cannabinoids: The Current State of Evidence and Recommendations for Research. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
Medical News Today. 2020. What to know about Terpenes. Accessed from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com
Medical News Today. 2020. What’s the difference between indica and sativa? Accessed from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com
An Introduction to the Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
Your body naturally creates substances called endocannabinoids, and some of these are similar to the cannabinoids found in marijuana.
The body’s ECS sends “signals” (endocannabinoids) to “receivers” (CB1 and CB2 receptors) to help balance your body’s sleep cycle, appetite level, and more.
The cannabinoids in marijuana act in a similar way by connecting to the CB1 and CB2 “receivers” which can lead to different effects (e.g., increased appetite, changes in mood). But cannabinoids in marijuana are not identical to human cannabinoids and they are not the only component of marijuana.
It is not yet completely understood whether and how medical marijuana may help with a number of medical conditions.

CB1 Receptor

CB2 Receptor
How the Body’s ECS Works
Central Nervous System
Supports the brain and central nervous system including increasing memory
Immune System
Affects the immune system to reduce inflammation.
Hormones
Balances hormones that support metabolism, reproduction, and stress levels.
Digesting Food
Helps control irritation and inflammation in your digestive system.
Muscles
Helps control blood sugar. Creates a feeling similar to a “runner’s high”.
Bones
Supports bone mass and strength.
Please note: This page is for informational purposes only, but is not medical or legal advice and should not be used to make healthcare decisions. Please consult your healthcare provider to find out what treatment options are available for you.
Updated May 2021
SOURCES:
Ligresti A, De Petrocellis L, Di Marzo V. From Phytocannabinoids to Cannabinoid Receptors and Endocannabinoids: Pleiotropic Physiological and Pathological Roles Through Complex Pharmacology. Physiol Rev. 2016;96(4):1593-659.
Wilson RI, Nicoll RA. Endocannabinoid signaling in the brain. Science. 2002;296(5568):678-82.
Zlebnik NE, Cheer JF. Beyond the CB1 Receptor: Is Cannabidiol the Answer for Disorders of Motivation? Annu Rev Neurosci. 2016;39:1-17.
Greenwich Biosciences, Inc. 2019. The Difference Between THC and CBD: Endocannabinoid System. Accessed from www.cannabinoidclinical.com.
